Safeguarding Vulnerable Adults: Advocating for Their Protection
Estimated reading time: 14 minutes
One in every five adults experience abuse, neglect, and harm in their lifetime in the UK according to Domestic Abuse Statistics UK. Ensuring the safety and wellbeing of vulnerable adults is a cornerstone of a compassionate, ethical society. However, abuse, exploitation and neglect of at-risk groups still persists. Effective safeguarding is essential to protect the human rights of those unable to advocate for themselves. Safeguarding vulnerable adults must be a shared priority. It starts with understanding how important Safeguarding is to the society.
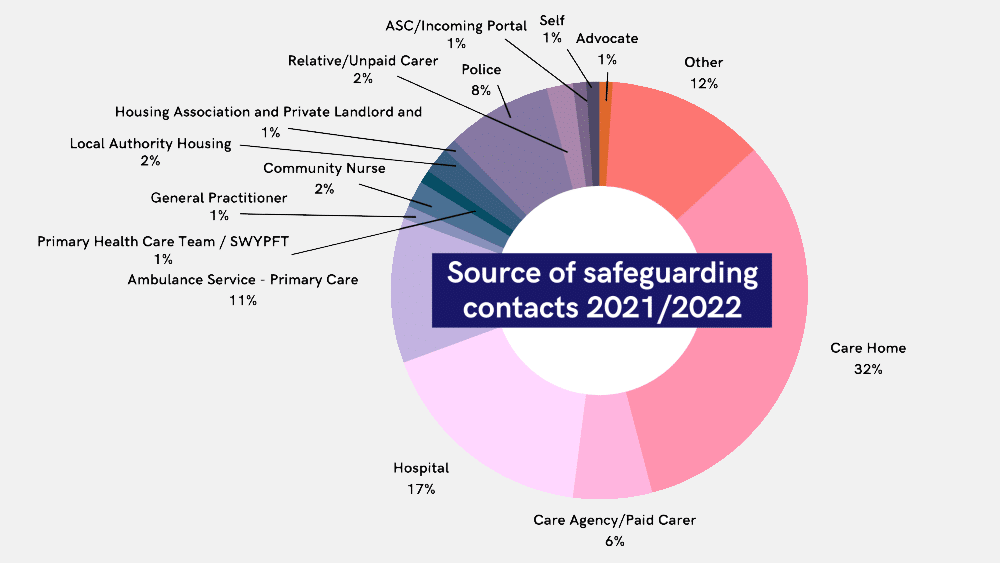
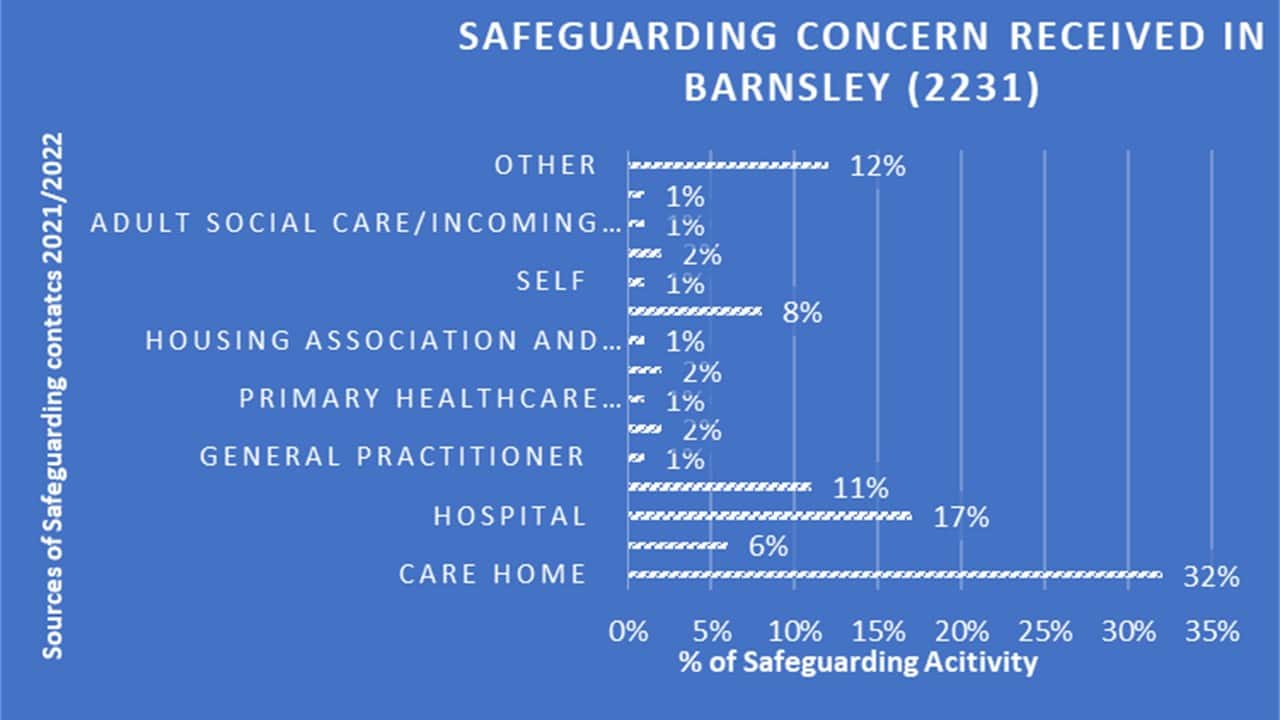
Barnsley Safeguarding Adults Board
In this article, we will explore the critical importance of safeguarding adults with care and support needs across the UK. We will examine why robust procedures and practices are needed, highlight key legislation, and outline how to properly report any concerns.
The goal is raising awareness so that all of us can contribute to a culture of vigilance and ensure every adult can live with dignity.
Table of Content for Safeguarding Vulnerable Adults
- What is Safeguarding Vulnerable Adults?
- Who are the most vulnerable adults in our society?
- Why is it important to Safeguard vulnerable Adults?
- Top 5 challenges vulnerable adults face
- The role of advocacy in protecting vulnerable adults
- How does the UK legal framework protect vulnerable adults?
- How to Report Safeguarding Vulnerable Adults
- The challenges of protecting vulnerable adults
- How can we address these challenges to protect at-risk adults?
- Five Key Pillars to Safeguarding Vulnerable Adults
What is safeguarding vulnerable adults?
Safeguarding vulnerable adults refers to a set of measures and actions that aim to protect adults at risk from harm, abuse, neglect or exploitation. These measures and actions taken protect adults due to their age, physical or mental disabilities, or other factors that make them vulnerable.
With the rise in abuse, harm, and neglect of vulnerable adults, the need for safeguarding is critical in order to reduce these figures.
The ultimate goal is enabling adults to live free from harm and fear. This requires a coordinated societal approach to identifying and addressing risks proactively.
Who are the most vulnerable adults in our society?
28 million adults in the UK are now considered vulnerable ( FCA Data, 2021).
Vulnerable adults encompass a diverse group of individuals who, due to various factors, are at increased risk of harm or exploitation. This can include elderly individuals, individuals with disabilities, those with mental health conditions, survivors of abuse or trauma, and individuals experiencing homelessness or poverty. Older adults are particularly at risk, with 63% of vulnerable adults being over the age of 65.
In identifying vulnerable adults, it involves recognizing signs of vulnerability such as physical or cognitive impairments, limited social support networks, dependence on caregivers, or experiences of abuse and neglect. It’s crucial to adopt a compassionate and inclusive approach, acknowledging that vulnerability can be fluid and that individuals may transition in and out of vulnerable situations throughout their lives. It’s important to adopt a compassionate and inclusive approach, recognising that vulnerability can be fluid and that individuals may transition in and out of vulnerable situations throughout their lives.
Why is it important to safeguard vulnerable adults?
Safeguarding requires a shared vigilance so that the most vulnerable members of society are not left isolated and exposed to preventable harm. A compassionate and just system depends on safeguarding.
key reasons why safeguarding vulnerable adults is critically important:
- Protects their human rights – Every adult deserves to live free from abuse, harm or neglect regardless of disability or capacity. Safeguarding upholds dignity.
- Prevents suffering – Safeguarding stops vulnerable people enduring physical, emotional or financial distress from maltreatment.
- Saves lives – In some cases, ending abuse can be life-saving. Safeguarding aims to prevent the most tragic outcomes.
- Promotes wellbeing – Feeling safe and supported enables greater wellbeing and fulfillment. Safeguarding fosters healthy lifestyles.
- Allows informed choices – With the right support, vulnerable adults can maintain independence and manage risks themselves.
- Provides recourse – Safeguarding procedures ensure concerns are properly investigated and victims given support.
- Deters perpetrators – Stringent safeguards discourage would-be abusers fearful of consequences.
- Reassures families – Safeguarding comforts relatives who cannot be constant protectors.
- Fulfills duty of care – Service providers, caregivers and society have an obligation to ensure safety.
What challenges do vulnerable people face?
Vulnerable people face a multitude of challenges that can impact their well-being and safety. These challenges may include limited access to resources and support, social isolation, discrimination, abuse, neglect, and barriers to healthcare and education.
In addition, addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure the protection and empowerment of vulnerable individuals in our society.
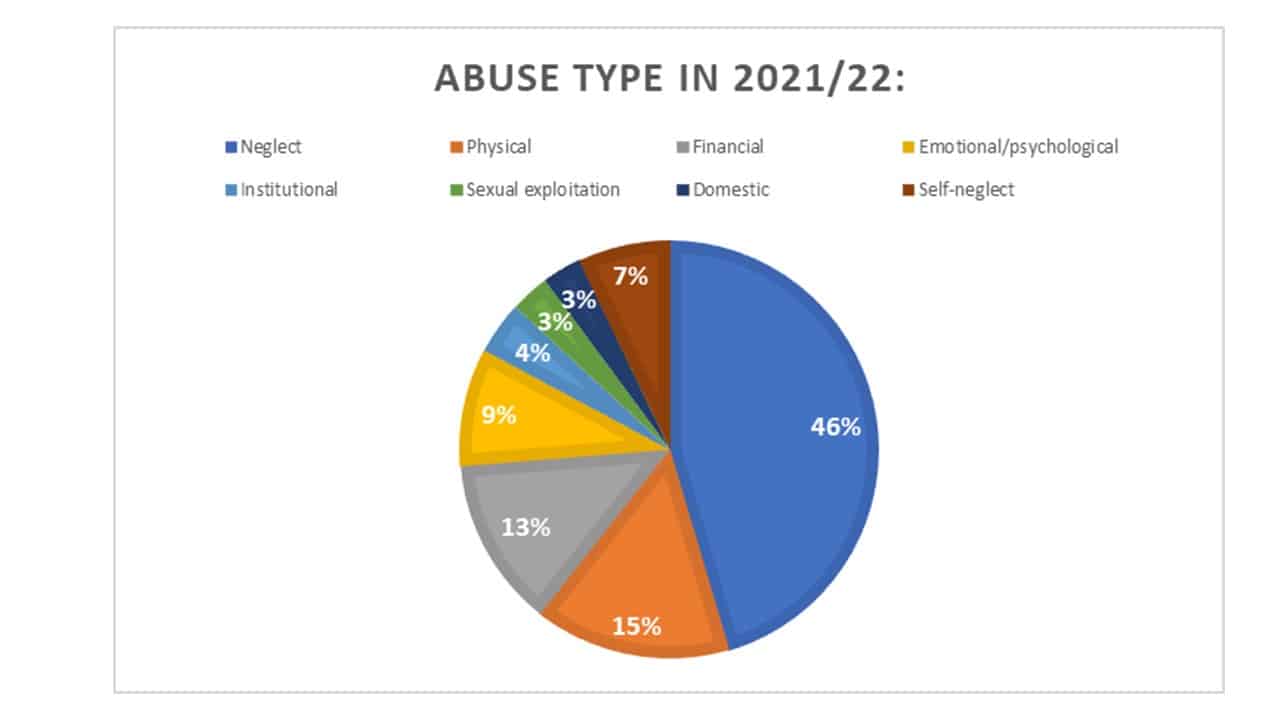
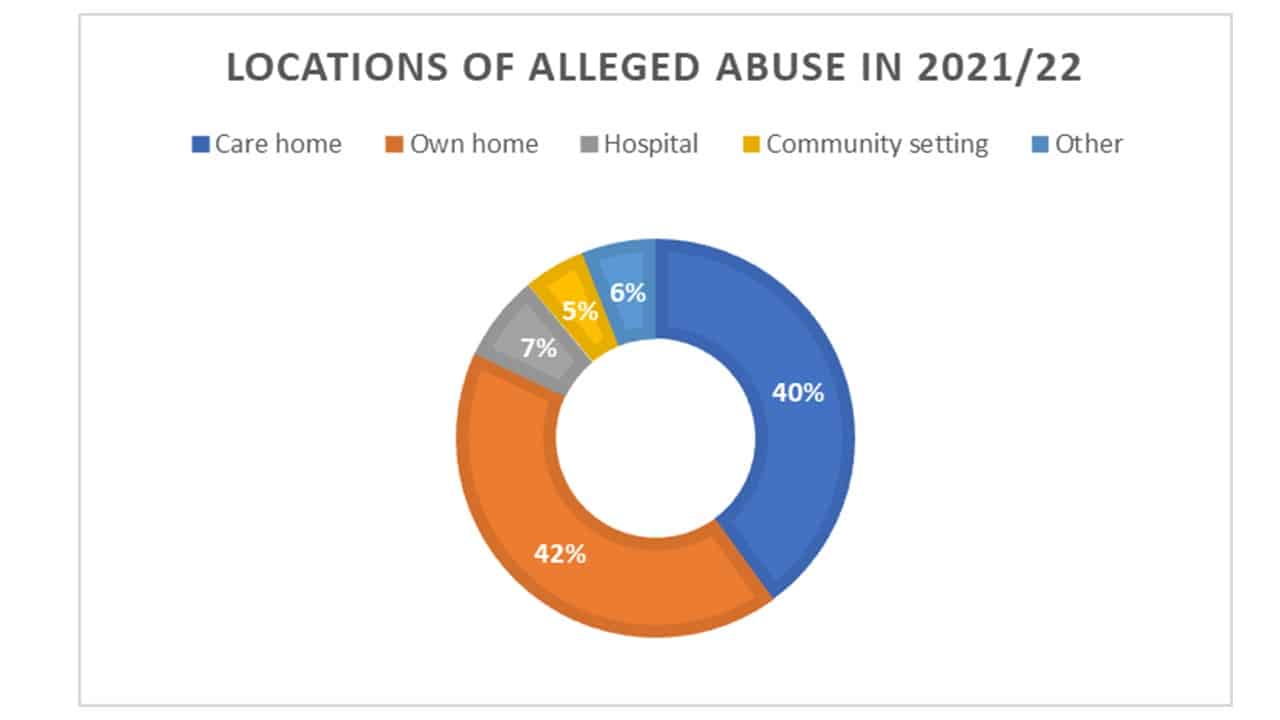
Barnsley Safeguarding Adults Board
Top 5 challenges vulnerable adults face
Vulnerable adults face a range of challenges and risks that can significantly impact their well-being and overall quality of life:
1. Abuse and neglect:
Vulnerable adults are susceptible to physical, emotional, and financial abuse, as well as neglect by caregivers or institutions responsible for their care. In 2020-21, concerned individuals raised 498,260 cases of abuse regarding vulnerable adults. (NHS, Safeguarding Adults, England, 2021-22)
2. Financial exploitation:
Individuals with limited financial resources or cognitive impairments are particularly vulnerable to exploitation, including scams, fraud, and undue influence.
3. Social isolation:
Many vulnerable adults face social isolation and loneliness, often due to limited mobility, lack of access to transportation, or diminished social networks. This isolation can contribute to a decline in mental and physical health.
4. Limited access to healthcare:
Vulnerable adults may encounter barriers in accessing healthcare services, resulting in inadequate medical attention and untreated health conditions.
5. Discrimination and stigma:
Individuals with disabilities or mental health conditions may face discrimination and stigmatization, which can further marginalize and isolate them from society.
The vulnerability experienced by adults in these situations has a profound impact on their well-being and overall quality of life. The lack of support and protection exposes them to physical and emotional harm, erodes their autonomy and dignity, and hinders their ability to live fulfilling and independent lives.
The stress and trauma resulting from their vulnerability can contribute to the deterioration of their mental and physical health, exacerbating existing conditions and hindering recovery.
Moreover, the societal marginalisation and exclusion faced by vulnerable adults perpetuate cycles of disadvantage and prevent them from accessing the resources and opportunities they need to thrive.

How can a Social Worker Safeguard Vulnerable Adults?
Social workers play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of vulnerable adults. As a social worker, you can follow these series of steps to identify and protect individuals who may be at risk due to factors like age or disabilities.
Here are the 12 steps you can take as a social worker to safeguard vulnerable adults within your vicinity:
1: Identify Vulnerability
- First, you need to recognise individuals who may be vulnerable due to factors like age or disabilities.
2: Assessment
- Conduct assessments. This means evaluating each person to understand how vulnerable they are and what they need.
3: Build Trust
- Building trust is key. You want the person to feel comfortable talking to you.
4: Risk Assessment
- Look for potential risks like abuse or neglect by observing their living conditions and talking to them.
5: Care Plan
- Create a personalised care plan. Think of this as a roadmap for their well-being. Include the person in planning their care.
6: Support Services
- Arrange services they need, like medical help or counseling.
7: Regular Check-Ins
- Schedule regular visits to make sure they’re safe and well.
8: Documentation
- Keep careful records of everything, from assessments to any concerns or incidents.
9: Reporting Concerns
- If you think someone is being abused or neglected, report it following the rules of your agency.
10: Collaboration
- Work with other professionals, agencies, and the person’s support network to keep them safe.
11: Empowerment
- Help them make decisions about their life and care. Empower them to have a say.
12: Review and Adjust
- Periodically, review the care plan. Make changes as needed to ensure their safety and happiness.
These steps ensure that social workers can effectively safeguard vulnerable adults, making a positive impact on their lives.
What is the role of advocacy in protecting vulnerable adults?
Advocacy refers to the active support and representation of the rights, needs, and well-being of vulnerable adults. It involves speaking up on behalf of vulnerable individuals, raising awareness about their challenges, and working towards systemic changes that promote their safety, autonomy, and inclusion. Advocacy encompasses a range of activities, including policy reform, community education, direct support, and empowerment of vulnerable adults themselves.
Advocacy plays a critical role in safeguarding the rights and well-being of vulnerable adults.
It amplifies the voices of those who are often marginalised and unheard. By giving a platform to vulnerable adults and their experiences, advocacy challenges societal norms and attitudes that perpetuate their vulnerability and exclusion. It raises awareness and shifts public perception, fostering empathy, understanding, and support.
Advocacy also serves as a catalyst for change at both individual and systemic levels. Advocates can address the gaps and weaknesses in existing systems that fail to adequately support vulnerable adults. They do this by advocating for policy reforms, seeking stronger legal protections, and pushing for improved services.
Through these efforts, advocates aim to bring about positive changes and ensure better support for vulnerable adults. Advocacy, through working with policymakers, service providers, and community organizations, can drive positive shifts in practices. This helps ensure that the rights and well-being of vulnerable adults are prioritized and protected.
How does the UK legal framework protect vulnerable adults?
In the United Kingdom, the protection of vulnerable adults is supported by a comprehensive legal framework and a range of policies. The key legislation includes:
1. Care Act 2014:
The Care Act 2014 is a legislation that outlines the legal duties and responsibilities of local authorities. It focuses on providing care and support for adults with care and support needs. It emphasizes person-centred care, safeguarding, and the promotion of well-being.
2. Mental Capacity Act 2005:
This act provides a framework for decision-making on behalf of adults who lack the capacity to make specific decisions. It establishes safeguards to ensure decisions are made in the best interests of the individual while promoting their autonomy and dignity.
3. Equality Act 2010:
This act prohibits discrimination on the grounds of disability, age, or other protected characteristics. It ensures that vulnerable adults are protected from unfair treatment and have equal access to services, employment, and opportunities.
While the existing legal frameworks in the UK provide a solid foundation for protecting vulnerable adults, their effectiveness is subject to ongoing evaluation and improvement. Assessing the extent to which laws and policies are effectively implemented and enforced is essential. This assessment should cover different regions and sectors. This involves examining issues such as consistency, resource allocation, and training for professionals involved in safeguarding.
It’s important to ensure that information and resources for vulnerable adults and their caregivers are readily available. Additionally, they should be easy to understand for all groups and demographics. Strengthening partnerships between different agencies, including social care services, GPs, police, and community organizations is crucial. It may improve the care and protections we can offer to vulnerable adults.
How to report safeguarding vulnerable adults
If you are concerned about the safety or well-being of a vulnerable adult, you can report it to the appropriate authorities. The following are the ways to report safeguarding vulnerable adults in the UK:
- If the person is in immediate danger, contact emergency services on 999.
- If the concern is urgent but not an emergency, contact Adult Social Services in your local area. You can do a search here to find one within your location, click this link.
- Clearly describe the specific concern, providing key details like names, dates and what occurred. Stick to only factual information.
- If contacting by phone, follow up the verbal report with a written account via email or using an incident report form.
- For non-urgent concerns, reporting can also be done using Adult Social Service’s online forms or email if available.
- When reporting, include any evidence that supports the concern, such as photographs of injuries or screenshots of messages. But do not attempt to investigate yourself.
- Identify any additional agencies involved with the vulnerable adult that should be informed.
- Maintain confidentiality. Only share details with the adult safeguarding team and other necessary agencies.
- Be responsive to any requests for additional information from investigators.
Overall, the goal is to promptly alert authorities through proper channels so they can address threats to that vulnerable individual’s safety and wellbeing. Speaking up saves lives.
The challenges of protecting vulnerable adults
Protecting vulnerable adults isn’t always simple, in part because of the diverse challenges and risks that vulnerable adults face in every aspect of their lives. Let’s explore some of the difficulties that society must overcome to safeguard our most vulnerable members.
1. Financial exploitation and abuse
Vulnerable adults may be targeted by fraudsters, scammers, or even close acquaintances who take advantage of their limited financial literacy or cognitive impairments. Financial exploitation can result in significant financial losses, jeopardising their well-being and future security.
2. Neglect and inadequate care
Neglect and inadequate care pose a substantial risk to vulnerable adults. Due to various factors such as resource constraints, caregiver burnout, or lack of training, some individuals may experience neglect or receive substandard care. This can lead to physical harm, emotional distress, and worsening health conditions, undermining their overall well-being.
3. Social isolation and loneliness
Vulnerable adults often face social isolation and loneliness, which can have detrimental effects on their mental and physical health. Limited mobility, reduced social networks, and societal stigma contribute to their isolation. The lack of social connections and support networks exacerbates their vulnerability and diminishes their quality of life.
4. Lack of awareness and training among caregivers
Caregivers play a vital role in protecting vulnerable adults, but the lack of awareness and training among caregivers can hinder effective safeguarding. Many caregivers may lack the necessary knowledge to recognize signs of abuse or understand their legal obligations. Consequently, they may struggle to respond appropriately to the needs of vulnerable adults. For example, only 25% of carers are trained in safety and only 21% are trained in self-care (Caregiving.com survey, 2021).
How can we address these challenges to protect at-risk adults?
Addressing the challenges in protecting vulnerable adults requires a multi-faceted approach that combines various strategies. Increasing the availability of support services and providing additional training to caregivers and health professionals are essential steps. Additionally, strengthening legislation is crucial to specifically address the exploitation and neglect of vulnerable adults in order to ensure their protection.
Five Key Pillars to Safeguarding Vulnerable Adults
Strategies to safeguard vulnerable adults must incorporate elements of five key pillars:
1. Awareness:
Raising awareness about the rights, needs, and vulnerabilities of vulnerable adults is crucial for effective advocacy. Education campaigns targeted at the general public, caregivers, and professionals can help dispel myths, promote understanding, and foster a culture of empathy and support.
2. Collaboration:
Effective advocacy requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including government agencies, social services, healthcare providers, law enforcement, and community organizations. Strengthening these partnerships improves coordination, facilitates information sharing, and enhances the collective response to protect vulnerable adults.
3. Empowerment:
Empowering vulnerable adults to assert their rights and make informed decisions is essential. Providing accessible information, training in self-advocacy, and establishing support networks empower individuals. They can actively participate in decisions about their care, report abuse, and access necessary services.
4. Person-centred care and support:
By adopting a person-centred approach to care and support, we prioritize the needs, preferences, and goals of vulnerable adults. This approach places them at the center of service provision, ensuring their well-being and satisfaction. This approach promotes dignity, autonomy, and individualized support, minimising the risk of neglect and abuse.
5. Accountability:
Implementing robust mechanisms to monitor and assess the quality of care provided to vulnerable adults is crucial. Regular inspections, licensing requirements, and reporting systems are in place to help ensure that care providers meet necessary standards. Regular inspections, licensing requirements, and reporting systems hold care providers accountable for identified shortcomings.
By addressing these challenges and implementing effective strategies, we can strengthen advocacy efforts. This, in turn, allows us to provide comprehensive protection for vulnerable adults in our society.
Conclusion
Safeguarding the vulnerable should be everyone’s duty. While laws, policies and procedures create a framework, ultimately this effort relies on grassroots awareness and action.
We all must adopt a vigilant, compassionate mindset – whether through our work or community life. Look out for warning signs of abuse and neglect. Make appropriate notifications if concerns arise. But most importantly, see the humanity in every person regardless of their capacity.
Promoting dignity and respect in how we treat the most vulnerable individuals uplifts us all. With perseverance and shared diligence, we can create a society where no one falls through the cracks.
But it takes an unwavering commitment to safeguarding from each and every one of us. The wellbeing of vulnerable adults is our collective responsibility.
Let us Help you
We’ll help you find the right course for your needs. Tell us a little bit about your situation and what you would like to achieve.
We’ll get back to you within one working day.
