Exploring Confined Spaces: Understanding Hazards and Safety Measures
Are you aware of the dangers that lurk in confined spaces? It’s important to know that these areas can be extremely risky for those who enter them. Surprising statistics show that every year, a significant number of accidents and even deaths occur in these confined environments.
It’s shocking to think that a lack of awareness and inadequate safety measures can lead to such tragic outcomes. That’s why it’s crucial for us to understand the hazards associated with confined spaces and take necessary precautions to stay safe.
In this article, we will embark on a journey to uncover the hidden dangers of confined spaces and discuss essential safety measures that can truly make a difference. Together, let’s explore the facts, learn about the risks, and empower ourselves with the knowledge to navigate these challenging environments safely.
What we covered:
- Understanding Confined Spaces
- Examples of confined spaces
- Rules and Regulations in the UK
- Brief History of Regulation on confined spaces
- Golden rules of confined spaces
- Duration of Stay in Confined Spaces
- Types of Confined Spaces
- Recognizing Confined Spaces
- Hazard in Confined Spaces
- Safety Requirement and PPE
- What not to do in Confined Spaces
- Respirators in Confined Spaces
- Hazards in Confined Spaces
- Air Testing in Confined Spaces
- The 2*2 Rules of Confined Spaces
- The Danger of Methane Gases
- Confined Space Risk Assessment and Hazard
Understanding Confined Spaces:
Defining confined spaces and their characteristics.
Confined spaces are areas that have limited entry and exit points, restricted ventilation, and the potential for hazardous conditions. They can be found in various work environments, such as industrial sites, construction sites, and even underground tunnels. It is crucial to understand the characteristics of confined spaces to ensure safety in these environments.

Image by aleksandarlittlewolf on Freepik
Examples of Confined Spaces:
When we talk about confined spaces, we are referring to areas like storage tanks, silos, tunnels, crawl spaces, and sewers. These spaces often have narrow openings and are not designed for continuous human occupancy. Due to their restricted nature, confined spaces can pose significant risks to workers if proper precautions are not taken. Some examples of risks associated with confined spaces include exposure to toxic gases, lack of oxygen leading to asphyxiation, the potential for fires or explosions, and the risk of entrapment or engulfment. It is crucial to prioritize safety measures and follow proper protocols to mitigate these risks and ensure the well-being of workers in confined spaces.
Importance of Recognizing Confined Spaces in different work environment:
Recognizing confined spaces is essential because they present unique hazards that may not be immediately apparent. The limited entry and exit points can make it challenging to evacuate in case of an emergency. Additionally, restricted ventilation in these spaces can lead to the accumulation of toxic gases, lack of oxygen, or the potential for fires and explosions.
It is crucial to be aware of confined spaces in different work environments. Whether it’s a construction site with trenches and excavations or an industrial facility with storage tanks, understanding the presence of confined spaces helps workers and employers implement necessary safety measures. By identifying these spaces, appropriate risk assessments and control measures can be put in place to ensure the well-being of workers and prevent accidents or injuries.
Remember, if you ever come across a space that seems cramped, has limited access points, or poses potential hazards, it’s important to treat it as a confined space and follow specific safety protocols. Understanding the characteristics of confined spaces and being aware of their presence can go a long way in promoting workplace safety.
Rules and Regulations in the UK:
Overview of the UK Regulations Governing Confined Spaces
Confined spaces are small and tight areas like tunnels or tanks. They can be dangerous, so the UK has rules called the Confined Spaces Regulations to keep people safe.
These rules help employers and workers know how to work in confined spaces without getting hurt.
The regulations say that employers must plan and prepare before going into a confined space. They need to figure out if the space is confined and check for any risks.
They should also give workers training and the right safety equipment, like special clothing or breathing devices.
Workers have a responsibility too. They must follow their employer’s instructions and use the safety equipment correctly.
They need to know the signs of danger, like not having enough air or being near toxic gases.
Confined Space Regulations
The UK government made these regulations to protect workers and prevent accidents in confined spaces. It’s important for both employers and workers to know and follow these rules to stay safe.
1997: The introduction of the Confined Spaces Regulations 1997 to establish legal requirements for worker safety in confined spaces.
2003: Revision of the regulations to enhance safety practices. This follows a tragic incident where four workers died in a confined space due to exposure to toxic gases.
2010: Updates to the regulations to provide clearer guidance on risk assessment, emergency planning, and communication procedures.
The Confined Space Regulations were put in place to make sure workers stay safe in small, tight spaces. Employers have important responsibilities to follow these rules.
They must identify and assess confined spaces to understand any risks. They also need to give workers training and use safety measures to protect them.
The regulations have been updated over time to improve safety standards and prevent accidents.
This shows that the government cares about keeping workers safe and wants to avoid any harm in confined spaces.
A brief history of Regulation on confined space in the UK
Confined space regulations in the UK have changed over time to make sure people working in tight spaces are safe. In 1997, the Confined Spaces Regulations were made to protect workers. Before that, accidents happened because there were no specific rules. For example, in 1988, a fire in King’s Cross station killed 31 people. This made everyone realize the need for better safety.
The 1997 regulations told employers they had to check confined spaces, give training, and use safety measures. But accidents still happened, so the rules were updated in 2003. Four workers died because of toxic gases in a sewage plant. This made the rules even stricter.
Throughout the years, these regulations have been changed to improve safety and prevent accidents. In 2010, the rules were updated again to give clearer instructions on how to assess risks and plan for emergencies.
These changes show that the government cares about workers’ safety and wants to make sure accidents are avoided in confined spaces.
Brief Statistics on Confined Space
Did you know that more than 60% of people who try to rescue others in tight spaces end up getting hurt or even killed? It’s important to be aware of this because it’s a major problem. In the United States, there are over 4.8 million occasions every year when people have to go into these small, cramped spaces for different reasons.
To make sure everyone stays safe in these situations, there are special rules from a group called OSHA. These rules say that employers must have a written plan for going into these tight spaces and teach their workers how to stay safe.
OSHA also has guidelines for the amount of oxygen that should be in these spaces. They say there should be at least 19.5% oxygen and no more than 23.5% oxygen to prevent accidents and keep people from getting hurt. Source (Wikipedia)
Employer and Employee Responsibilities in Ensuring Compliance with Safety Guidelines.
To make sure everyone stays safe, both employers and employees have important responsibilities when it comes to following safety guidelines.
Employers have a big role to play. It’s their job to provide a safe working environment for their employees. This means they need to identify any potential hazards and take steps to control or eliminate them. Employers should provide proper training to employees, teaching them how to stay safe and use safety equipment correctly. They should also make sure that all necessary safety measures are in place, such as emergency plans and protective gear. Employers must regularly inspect the workplace to ensure it meets safety standards and address any issues promptly.
On the other hand, employees also have responsibilities to ensure compliance with safety guidelines. They should follow their employer’s instructions and use safety equipment as instructed. It’s crucial for employees to report any unsafe conditions or hazards they notice to their employer. They should take the necessary precautions to protect themselves and their coworkers, such as wearing personal protective equipment and using safety devices.
Compliance with safety guidelines requires a partnership between employers and employees. Employers must provide a safe environment and the necessary resources, while employees must actively participate in safety practices and follow the guidelines. By working together, everyone can contribute to creating a safe and healthy workplace.
Golden Rules of Confined Spaces
Essential Principles for Working in Confined Spaces
When working in confined spaces, it’s important to follow some essential principles to stay safe. Here are a few key ones to remember:
Proper training: Before entering a confined space, make sure you have received proper training. Learn about the potential hazards, safety procedures, and how to use safety equipment. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions and stay safe.
Example: Imagine you’re working in a small boiler room. Before entering, you check that there is good airflow and that any exhaust systems are working properly. This ensures a sufficient supply of fresh air, reducing the risk of suffocation or exposure to harmful gases.
Communication: Always stay in touch with your team members or someone outside the confined space. Let them know your location, and how long you plan to be inside and establish a communication plan in case of an emergency. This way, help can reach you quickly if needed.
Continuous Monitoring for Safety
Continuous monitoring is crucial when working in confined spaces. Here’s why:
Proper ventilation: Confined spaces can have limited airflow, leading to a lack of oxygen or the accumulation of harmful gases. Ensure that the confined space is properly ventilated before entering. This will help maintain a safe level of oxygen and remove hazardous fumes.
Gas detection: Carry a portable gas detector with you to monitor the air quality inside the confined space. This device can alert you if there are dangerous levels of toxic gases present, allowing you to take necessary precautions or evacuate if needed.
Example: Picture yourself inside a storage silo. As you enter, you use a handheld gas detector to check for any dangerous gases like methane or carbon monoxide. If the detector indicates high levels of these gases, you quickly exit and inform the appropriate personnel to address the issue.
Emergency Preparedness
Being prepared for emergencies is essential in confined spaces. Consider the following:
Emergency rescue plan: Have a well-defined rescue plan in place before entering a confined space. Make sure everyone knows their roles and responsibilities in case of an emergency. This will ensure a prompt and effective response to any unforeseen situations.
Ex: Imagine you are part of a team inspecting a sewer system. Before entering, you review the rescue plan that outlines who will perform the rescue, the equipment required, and the steps to follow in case someone gets injured or trapped.
Personal protective equipment (PPE): Wear the appropriate PPE, such as a safety harness, helmet, and protective clothing, as per the requirements of the confined space. PPE can provide added protection and increase your chances of staying safe in case of an emergency.
Ex: Picture yourself inside a storage tank. Before entering, you wear a safety harness, helmet, and protective clothing. These precautions provide a layer of protection and increase your chances of staying safe in case of a fall or other accidents.
Following these golden rules will help you stay safe and minimize the risks associated with working in confined spaces.
Click Link: Unlock the key to safe work in confined spaces – Enroll in our comprehensive Confined Space Training today!–3 years Certification.
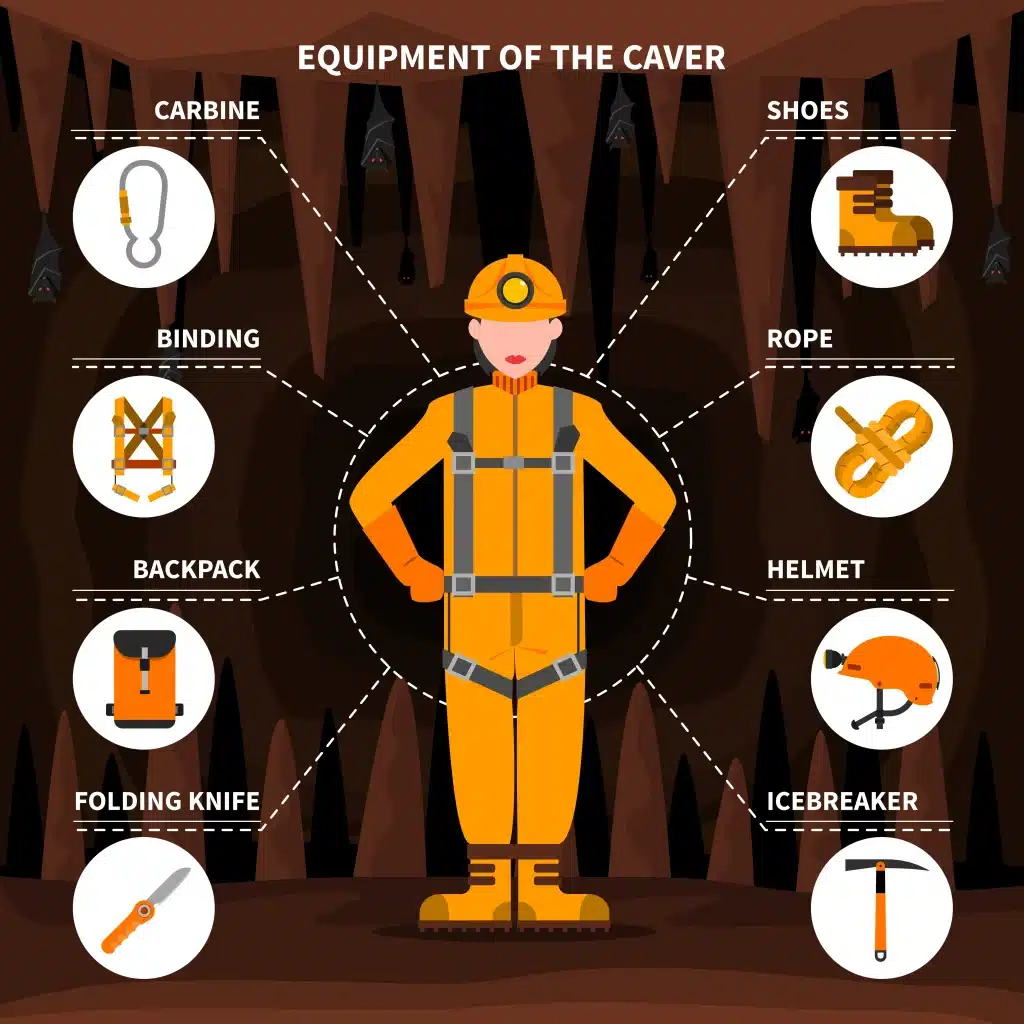
Image by macrovector on Freepik
Duration of Stay in Confined Spaces
Exploring Factors that Determine Permissible Duration of Stay
When working in confined spaces, it’s crucial to understand how long it’s safe to stay inside. Several factors determine the permissible duration of stay. Here are some things to consider:
Air quality: The quality of the air inside a confined space is essential for your safety. Harmful gases or lack of oxygen can be present. Proper ventilation and continuous monitoring help ensure the air remains safe to breathe. If the air quality deteriorates, it’s important to limit your time inside or evacuate.
Illustration of duration in confined spaces:
Imagine you’re working in a small storage room. You need to ensure that the air you breathe is clean and free from harmful gases. If you notice a strange smell or feel dizzy, it could mean the air quality is not safe, and you should limit your time inside or leave immediately.
Oxygen levels: Oxygen is necessary for us to breathe properly. In confined spaces, it’s important to monitor the oxygen levels. The minimum safe level of oxygen is around 19.5%, and the maximum safe level is approximately 23.5%. If the oxygen level drops below the minimum or rises above the maximum, it can be dangerous and may limit the time you can spend inside.
Potential hazards: Confined spaces can pose various hazards such as toxic gases, flammable materials, or physical obstructions. These hazards can increase the risks associated with prolonged exposure. Understanding the potential risks and taking necessary precautions are vital for determining the duration of stay.
Illustration 2: Using a tank as a reference
Picture yourself inside a tank. It’s crucial to check the oxygen levels using a device called an oxygen meter. If the oxygen level drops too low, it can make it hard for you to breathe properly, and you might need to leave the confined space to get fresh air.
Suppose you’re working in a sewer system. There might be hazardous materials like chemicals or sewage present. It’s important to be aware of these potential dangers and follow safety procedures to protect yourself. If you notice any signs of danger, it’s better to limit your time inside or get out to ensure your well-being.
Importance of Monitoring Air Quality, Oxygen Levels, and Hazards
Monitoring air quality, oxygen levels, and potential hazards is essential to ensure your safety while working in confined spaces. Here’s why:
Air quality: Regularly monitoring the air quality helps detect any changes that might indicate the presence of harmful gases or lack of oxygen. This allows you to take necessary actions to protect yourself and limit your time inside if needed. For example, if you’re painting inside a small room, you should ensure proper ventilation to prevent inhaling fumes that can be harmful to your health.
Oxygen levels: Monitoring oxygen levels ensures that the air you breathe contains enough oxygen to keep you safe and healthy. If the oxygen levels drop too low or rise too high, it can cause dizziness, difficulty breathing, or even loss of consciousness. If you’re working in a basement or cellar, you might need to open windows or use fans to bring in fresh air and maintain a safe oxygen level.
Potential hazards: Continuously monitoring for potential hazards helps identify any emerging dangers in the confined space. This allows you to address the hazards promptly and take appropriate measures to stay safe. For instance, if you’re working in a confined space that contains electrical equipment, it’s important to be cautious and avoid contact with live wires to prevent electrical accidents.
Paying attention to air quality, oxygen levels, and potential hazards in confined spaces is vital for determining how long it’s safe to stay inside. Always prioritize your safety and follow the guidelines to minimize risks during your work.
Types of Confined Spaces
Examining Different Types of Confined Spaces
When it comes to confined spaces, there are several types that you might encounter in workplaces. Let’s explore a few common ones:
Tanks and vessels: These are large containers like storage tanks or silos. They are usually closed and have limited openings, making it difficult to enter or exit.
Tunnels and ducts: These are narrow passages underground or within buildings used for transportation or utility systems. They can be tight and cramped, making movement challenging.
Sewers and manholes: These are underground tunnels used for drainage and sewage systems. They can be small and filled with water or harmful gases.
Pipelines and shafts: These are long pipes or vertical openings used for transporting liquids, gases, or people. They can have confined spaces within them, such as inspection pits or control rooms.
Discussing Characteristics and Specific Hazards
Each type of confined space comes with its own characteristics and specific hazards. Here are a few examples:
Tanks and vessels: These spaces can lack proper ventilation, leading to a build-up of toxic gases or a decrease in oxygen levels. They can also have chemicals or flammable materials inside, increasing the risk of fires or explosions.
Tunnels and ducts: These spaces can have limited visibility and poor air circulation. They may also contain obstacles like cables or pipes that can cause trips or falls. Additionally, there’s a risk of encountering hazardous materials or getting trapped in case of a collapse.
Sewers and manholes: These spaces often have poor air quality due to sewage gases, which can be harmful to breathe. They can also be filled with water, posing a drowning hazard. The presence of bacteria or viruses in sewage can also lead to health risks.
Pipelines and shafts: These spaces can be narrow and difficult to navigate. There’s a risk of getting stuck or injured while moving through them. Additionally, there might be dangers like pressure hazards, hazardous substances flowing through the pipes, or the risk of falling from heights.
It is important to be aware of the different types of confined spaces and their associated hazards. By understanding these characteristics, you can take necessary precautions and stay safe when working in such environments.
Start your Journey in Health and Safety Practice with our: Health and Safety Online Training
Recognizing Confined Spaces
Identifying the Three Key Factors
When it comes to recognizing confined spaces, there are three important factors to consider. Let’s take a closer look at each one:
Limited entry and exit: Confined spaces are places that have small openings or tight access points. It means that getting in and out of these spaces can be challenging. Examples include storage tanks, crawl spaces, or even a small room with only one door.
Restricted ventilation: Confined spaces often have limited airflow, which means fresh air can’t easily come in or stale air can’t escape. This lack of proper ventilation can lead to poor air quality, making it harder to breathe inside. Think of a small basement or a tunnel with no windows or vents.
Potential for hazardous atmospheres: Confined spaces can have the potential for dangerous situations. They may contain harmful gases, chemicals, or substances that can cause harm or even be life-threatening. For instance, a storage tank may have toxic fumes, or a sewer system can release dangerous gases.
By considering these three factors –
- limited entry and exit,
- restricted ventilation, and
- potential for hazardous atmospheres – you can identify whether a space is confined or not.
It’s important to recognize confined spaces because they require special safety measures and precautions to ensure your well-being.
Remember, if you find yourself in a confined space, always prioritize your safety and follow the necessary guidelines to protect yourself and others around you.
Hazards in Confined Spaces
Exploring Potential Hazards
When working in confined spaces, there are several potential hazards that you need to be aware of. Let’s take a closer look at some of these hazards:
Toxic gases: Confined spaces can contain gases that are harmful to breathe, such as carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, or methane. These gases can be odorless and invisible, making them difficult to detect without proper monitoring equipment.
Lack of oxygen: Some confined spaces may have a limited supply of oxygen, making it hard to breathe properly. This can happen in spaces like storage tanks or underground tunnels. Without enough oxygen, you may experience dizziness, difficulty breathing, or even lose consciousness.
Fire and explosion risks: Certain confined spaces can pose a risk of fires or explosions. This can be due to flammable materials, chemicals, or improper storage of combustible substances. The confined nature of these spaces can increase the intensity and spread of fires or explosions.
Physical hazards: Confined spaces can also present physical hazards. These can include obstacles like pipes, cables, or machinery that can cause trips, falls, or injuries. Limited visibility and cramped spaces can make it challenging to navigate safely.
Importance of Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment, and Control Measures
Identifying, assessing, and controlling hazards in confined spaces is crucial for your safety. Here’s why:
Hazard identification: Recognizing potential hazards helps you understand the risks associated with a confined space. By being aware of the specific hazards present, you can take appropriate precautions and plan your work accordingly.
Risk assessment: Assessing the risks involved in a confined space allows you to determine the likelihood and severity of potential incidents. This helps prioritize safety measures and implement controls to reduce the risks to an acceptable level.
Control measures: Implementing control measures helps minimize or eliminate the identified hazards. These measures can include proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), safety procedures, and regular monitoring to ensure a safe working environment.
Understanding the hazards in confined spaces and implementing appropriate control measures is essential for your safety. Always follow the guidelines, receive proper training, and communicate any concerns to ensure a safe working environment for everyone involved.
Safety Requirements and Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Detailing Necessary Safety Measures and PPE
When it comes to working in confined spaces, there are important safety measures and personal protective equipment (PPE) that you need to know about. Let’s take a closer look:
Appropriate clothing: It’s important to wear the right kind of clothing when entering confined spaces. This includes wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and sturdy shoes or boots that provide protection. Proper clothing can help shield your body from potential hazards like chemicals, sharp objects, or rough surfaces.
Respiratory protection: In some confined spaces, the air might be filled with harmful gases or have low oxygen levels. To protect your lungs, you may need to wear a mask or respirator that filters the air you breathe. This helps ensure you have clean and safe air to breathe while working.
Fall protection equipment: Confined spaces can sometimes have high places or areas where you could fall from a height. To prevent accidents, using fall protection equipment like harnesses and safety lines is essential. These tools keep you secure and prevent falls that could result in injuries.
Importance of Wearing Appropriate Clothing, Respiratory Protection, and Fall Protection Equipment
Wearing the right clothing and using the necessary protective equipment is crucial for your safety when working in confined spaces. Here’s why:
Appropriate clothing: Wearing the right clothes protects your body from potential injuries and hazards. It can prevent cuts, scratches, or burns from sharp objects or chemicals. Proper clothing also helps you move comfortably and safely in confined spaces.
Respiratory protection: Breathing in harmful gases or substances can be dangerous for your health. Wearing a mask or respirator filters the air and prevents you from inhaling these harmful particles. It ensures that the air you breathe is clean and safe.
Fall protection equipment: Working in confined spaces may involve climbing or being in elevated areas. Fall protection equipment, like harnesses and safety lines, keeps you safe by preventing falls. They provide a lifeline that secures you and prevents accidents that could cause serious injuries.
Remember, wearing appropriate clothing, using respiratory protection, and utilizing fall protection equipment are essential safety measures in confined spaces. By following these guidelines and using the right equipment, you can protect yourself and reduce the risk of accidents or injuries while working.
What Not to Do in Confined Spaces
Addressing Common Mistakes and Unsafe Practices
When it comes to working in confined spaces, it’s crucial to be aware of what not to do. Let’s take a closer look at some common mistakes and unsafe practices:
Working alone: One of the biggest mistakes is working alone in a confined space. It’s important to have someone else nearby who can help in case of an emergency. Working alone increases the risk of accidents and can make it harder to get help if something goes wrong.
Neglecting safety protocols: Ignoring or neglecting safety protocols can be extremely dangerous. Safety protocols are put in place to protect you and ensure your well-being. Always follow the guidelines and procedures set by your employer or safety regulations.
Improper use of equipment: Using equipment improperly can lead to accidents or injuries. It’s important to receive proper training on how to use the equipment safely. Using equipment without the necessary knowledge or not following instructions can put you and others at risk.
Promoting Awareness about Risks
It’s crucial to be aware of the risks associated with the aforementioned mistakes and unsafe practices. Here’s why:
Working alone: Working alone in a confined space means there is no one nearby to assist you in case of an emergency. If something goes wrong, it can be challenging to get help or receive immediate medical attention. Having a buddy system or working with a team ensures that someone is there to assist you if needed.
Neglecting safety protocols: Safety protocols are designed to keep you safe and prevent accidents. Ignoring these protocols can lead to serious injuries or even fatalities. It’s important to always follow safety guidelines, such as wearing personal protective equipment, communicating with others, and following proper entry and exit procedures.
Improper use of equipment: Equipment is meant to make your work easier and safer. However, using equipment improperly or without proper training can lead to accidents or malfunctions. Always take the time to learn how to use the equipment correctly and follow instructions provided by manufacturers or supervisors.
Note that understanding what not to do in confined spaces is just as important as knowing what to do. By avoiding these common mistakes and unsafe practices, you can help create a safer working environment for yourself and others.
Respirators in Confined Spaces
Discussing Types of Respirators Suitable for Confined Space Work
When working in confined spaces, using the right type of respirator is crucial for protecting your lungs from harmful gases and particles. Here are a few types of respirators suitable for confined space work:
Particulate respirators: These respirators are designed to filter out dust, mists, and other solid particles from the air you breathe. They are commonly used when there is no significant risk of gases or vapors in a confined space.
Gas and vapor respirators: These respirators are equipped with cartridges or filters that can remove specific gases or vapors from the air. They are suitable when you are working in a confined space where there is a potential for hazardous gases or vapors.
Self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA): SCBAs are the most protective type of respirators. They provide a supply of clean, breathable air from a tank worn on your back. SCBAs are typically used in high-risk confined spaces, such as those with low oxygen levels or high concentrations of toxic gases.
Emphasizing the Importance of Proper Fit-Testing, Maintenance, and Training
Using a respirator in a confined space requires more than just wearing it. Here’s why proper fit-testing, maintenance, and training are essential:
Fit-testing: It’s important to ensure that your respirator fits properly to create a seal and prevent contaminated air from entering. Fit-testing determines the right size and fit for your face. It should be done before using a respirator and periodically to ensure continued effectiveness.
Maintenance: Regular maintenance of respirators is vital to ensure they function correctly. This includes cleaning, inspecting, and replacing filters or cartridges as needed. Proper maintenance helps to keep the respirator in good working condition and ensures its effectiveness when you need it.
Training: Proper training on respirator use is crucial for your safety. You should be trained on how to put on and take off the respirator correctly, how to perform user seal checks, and how to maintain and store the respirator properly. Training also helps you understand the limitations of the respirator and the importance of using it in the right situations.
Remember, using the appropriate type of respirator, undergoing fit-testing, conducting regular maintenance, and receiving proper training are all important aspects of respirator use in confined spaces. By following these practices, you can ensure your respiratory health and stay protected from harmful gases and particles while working.
Air Testing in Confined Spaces
Why Air Testing and Atmospheric Monitoring are Important
When working in confined spaces, it’s crucial to test the air and monitor the atmosphere to keep everyone safe. Here’s why:
Checking oxygen levels: We need enough oxygen to breathe properly. Testing the air helps us make sure there’s the right amount of oxygen in the confined space. If there’s not enough oxygen, it can be hard to breathe and even make us feel dizzy or pass out. Testing helps us know if the air is safe to breathe.
Detecting toxic gases: Sometimes, confined spaces have gases that can harm us. These gases might not have any smell or color, so it’s hard to know if they’re there without testing. By testing the air, we can find out if there are any toxic gases. This way, we can take steps to protect ourselves and avoid getting sick from breathing in those harmful substances.
Watching out for flammable substances: In some confined spaces, there might be things that can catch fire or explode easily, like gases or vapors. Testing the air helps us find out if there are any flammable substances present. This helps us be careful and prevent accidents or fires from happening.
Why Regularly Checking Oxygen Levels, Toxic Gases, and Flammable Substances is Important
It’s important to keep checking the air in confined spaces regularly. Here’s why:
Breathing safely: Checking oxygen levels regularly helps us make sure there’s enough oxygen in the air for us to breathe safely. If there’s not enough oxygen, we need to bring in more air or use ventilation to keep it safe for us to be inside.
Staying healthy: Testing for toxic gases helps us know if there are any harmful substances in the air. By checking regularly, we can prevent breathing in these gases and protect our health. It helps us avoid getting sick or having problems with our lungs.
Preventing fires and explosions: Checking for flammable substances helps us know if there’s a risk of fire or explosion. By detecting these substances, we can take steps to make sure there are no sources of fire nearby and keep ourselves safe from accidents.
Take note that regularly testing the air and monitoring the atmosphere in confined spaces is important for our safety. By doing these checks, we can make sure the air is:
- safe to breathe,
- avoid harmful gases, and
- prevent accidents or fires from happening.
The 2*2 Rule of Confined Spaces
Understanding the Principle of the 2*2 Rule
When it comes to entering and exiting confined spaces safely, the 2*2 rule is an important principle to follow. Here’s what it means:
Two people nearby: Before entering a confined space, it’s crucial to have at least two people nearby. This means you should never go into a confined space alone. Having someone with you is important because they can help if something goes wrong or if you need assistance. They can call for help or rescue you if needed.
Constant communication: Communication is key when working in confined spaces. You should always be in constant communication with the person outside the confined space. This can be done using walkie-talkies or other communication devices. By staying in touch, you can let them know if there’s a problem or if you need help. They can also keep track of your progress and be ready to assist if necessary.
Importance of Having a Competent Person Nearby and Maintaining Constant Communication
Following the 2*2 rule is crucial for your safety. Here’s why it’s important:
Having a competent person nearby: A competent person is someone who is trained and knowledgeable about confined space work. Having a competent person nearby means you have someone who understands the risks and knows how to help if something goes wrong. They can assess the situation, provide guidance, and take appropriate actions to ensure your safety.
Maintaining constant communication: Constant communication with the person outside the confined space is essential. It helps them stay updated on your status and ensures that help can be provided quickly if needed. If you encounter any problems or feel unwell inside the confined space, they can coordinate rescue efforts or call for emergency assistance.
Note: The 22 rule is all about working together and staying connected when entering and exiting confined spaces. By following this rule, you can have someone nearby who can assist you in case of an emergency and maintain constant communication for a safer working environment.
Illustration on two-by-two rule on confined space:
Imagine you and your friend want to explore a deep, dark cave together. Before entering, you remember the 22 rule for confined spaces. You make sure there are at least two of you, never going alone. Your friend stays outside the cave, ready to help if anything goes wrong. You both have walkie-talkies to stay in constant communication. As you venture into the cave, you feel safer knowing that someone is watching out for you. If you encounter any problems, such as getting lost or feeling unwell, you can quickly call your friend for assistance. Following two-by-two rules keeps you both safe during your cave exploration adventure.
Danger of Methane Gases
Understanding the Risks Associated with Methane Gases in Confined Spaces
Methane gases can be dangerous when found in confined spaces. Let’s explore why:
Properties of methane: Methane is a type of gas that we cannot see or smell. It is highly flammable, which means it can easily catch fire or cause an explosion if there’s a spark or flame present. This makes it even more important to be cautious around methane gases.
Sources of methane: Methane can be found in various places. Natural processes, such as the decay of plants and animals, often produce methane. Methane can also be released from underground, like in coal mines or oil and gas wells. It’s important to be aware of these potential sources, especially in confined spaces where the gas can build up and become dangerous.
Potential health hazards: Breathing in methane gas can be harmful to our health. It can replace oxygen in the air, leading to a lack of oxygen for us to breathe properly. This can cause dizziness, difficulty breathing, and even unconsciousness. Methane gases can also mix with other chemicals in the air, forming harmful substances that can be toxic to our bodies.
Understanding the Importance of Methane Gas Awareness
It’s crucial to be aware of the dangers of methane gases in confined spaces. Here’s why:
Safety first: Knowing about the risks associated with methane gases helps us take necessary precautions to stay safe. By being aware of the properties and potential sources of methane, we can avoid actions that may cause a spark or ignite the gas, preventing accidents and keeping ourselves protected.
Proper ventilation: Understanding the presence of methane gases reminds us of the importance of proper ventilation in confined spaces. Ventilation systems help remove harmful gases and maintain a safe environment for us to work in.
Training and communication: Being aware of methane gas dangers emphasizes the need for proper training and communication. When working in confined spaces, it’s essential to receive training on recognizing and handling methane gases. Additionally, communicating with others about the presence of methane and any safety concerns is crucial for everyone’s well-being.
Methane gases can be hazardous in confined spaces. By understanding their properties, sources, and potential health hazards, we can take the necessary steps to ensure our safety. Being aware and informed helps us make smarter choices and stay safe when working in confined spaces.
Confined Space Risk Assessment and Hazards
Understanding the Process of Conducting a Confined Space Risk Assessment
When working in confined spaces, it’s important to assess the risks involved. Here’s how a risk assessment is done:
Identifying hazards: The first step is to identify potential hazards in the confined space. Hazards can include things like toxic gases, lack of oxygen, fire risks, or physical dangers like falling objects. By recognizing these hazards, we can understand what might harm us and take steps to prevent accidents.
Evaluating risks: Once hazards are identified, we assess the level of risk associated with each one. This means understanding how likely it is for a hazard to cause harm and how severe that harm could be. By evaluating risks, we can prioritize and focus on the most significant dangers.
Implementing control measures: After identifying hazards and assessing risks, we put control measures in place to reduce or eliminate them. This may involve measures like improving ventilation, using personal protective equipment (PPE), or establishing emergency procedures. These control measures help keep us safe while working in confined spaces.
Identifying Common Hazards and Control Measures
Here are some common hazards and the control measures to mitigate risks effectively:
Toxic gases: Proper air testing and monitoring help detect toxic gases. Ventilation systems remove the gases and ensure a safe breathing environment.
Lack of oxygen: Continuous monitoring of oxygen levels is crucial. If oxygen levels are low, we can implement additional ventilation or oxygen supply.
Fire risks: Eliminating potential ignition sources, such as sparks or open flames, is important. Fire extinguishers should be readily available, and workers should know how to use them.
Physical hazards: Keeping the area tidy and ensuring we properly secure objects prevents objects from falling or causing injuries. Personal protective equipment, such as hard hats and safety harnesses, can provide additional protection.
By following the risk assessment process and implementing control measures, we can reduce the risks associated with confined spaces and create a safer working environment. It’s important to be aware of hazards and take appropriate actions to protect ourselves and others when working in these spaces.
Conclusion:
It’s important to know about confined spaces and the dangers they can have. By following the rules and being aware of the risks, we can make sure everyone stays safe at work. Both employers and employees have a role to play. Employers need to give us proper training and talk to us about safety. They also must put safety measures in place. We need to communicate well with our team and follow the safety rules. Remember, training, communication, and following safety rules are super important when working in confined spaces. Let’s all work together to keep each other safe!
Let us Help you
We’ll help you find the right course for your needs. Tell us a little bit about your situation and what you would like to achieve.
We’ll get back to you within one working day.
